
Looking for the difference between production management and operations management? If yes, then we have got a perfect solution to your query. However, before we discuss the difference between these two terms, let’s learn about each in detail.
Whether a small cafe or an international fashion brand, no matter the size and type of industry, effective management is key to a successful and profitable business. It ensures the seamless functioning of operations and the successful delivery of products or services In the business world. However, for seamless management, Production management and Operations management (POM) play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency and ensuring the smooth functioning of a company. That’s not all! There is more than that. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the depths of Production and Operations Management, exploring their meaning, the key difference between production management and operations management, and much more.
So, without further ado, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
The Meaning of Production and Operations Management
At its core, Production and Operations Management focuses on the transformation of inputs into outputs through well-organized and controlled processes. This involves strategic decision-making to optimize resources, manage inventory, streamline production schedules, and enhance overall productivity.
POM involves a holistic approach, integrating various elements like technology, human resources, facilities, and information to create a well-coordinated production system. The ultimate goal is to minimize costs, maximize efficiency, and deliver high-quality products or services to customers.
An Overview of Production Management
Production Management primarily revolves around the manufacturing aspect of a business. It is a specialized field that deals with overseeing the creation of tangible goods. This involves coordinating and optimizing processes from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. Production Management is intricately connected to the shop floor, where the actual transformation of inputs into tangible outputs takes place.
Key Aspects of Production Management
Manufacturing Focus:
The core focus of Production Management is on the manufacturing processes involved in producing goods. This includes activities such as production planning, scheduling, quality control, and maintenance of machinery.
Resource Optimization:
Production Managers are tasked with efficiently utilizing resources such as labor, machinery, and raw materials to ensure that the production process is cost-effective and yields high-quality products.
Capacity Planning:
Planning and optimizing production capacity to meet demand are critical aspects of Production Management. This involves balancing the production output with market demand to avoid overproduction or shortages.
An Overview of Operations Management
Operations Management is a broader field that encompasses both manufacturing and service-related activities within an organization. It extends beyond the confines of the shop floor to include a comprehensive view of the entire operational system. Operations Management is concerned with designing, overseeing, and improving processes across the organization to ensure the efficient delivery of products or services.
Key Aspects of Operations Management
Holistic Approach:
Operations Management takes a holistic approach, addressing the overall management of processes involved in delivering a service or product. This includes everything from supply chain management to customer service.
Service Integration:
Unlike Production Management, Operations Management is not confined to tangible goods. It also involves the integration of various services, ensuring that both manufacturing and service-related functions work in harmony.
Strategic Planning:
Operations Managers engage in strategic planning to optimize organizational processes. This includes decisions related to capacity management, process design, and resource allocation across different departments.
Production Management vs Operations Management
While the terms “Production Management” and “Operations Management” are often used interchangeably, there are subtle distinctions between the two. Let’s learn about the basic difference between production management and operations management.

Production Management
Production Management primarily focuses on the manufacturing aspect of the business. It involves overseeing the actual creation of goods, from raw materials to the finished product. This includes activities such as production planning, scheduling, and quality control. In essence, Production Management is more concerned with the tangible aspects of the production process.
Operations Management
Operations Management, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses both manufacturing and service-related activities. It goes beyond the shop floor and extends to the overall management of processes involved in delivering a service or product. Operations Management includes strategic planning, capacity management, and the coordination of various functions within an organization.
Difference Between Production Management and Operations Management
Production Management and Operations Management are often mentioned in the context of organizational efficiency. However, these two closely related fields also have a few points of difference. Keep reading the blog to know the key difference between production management and operations management.
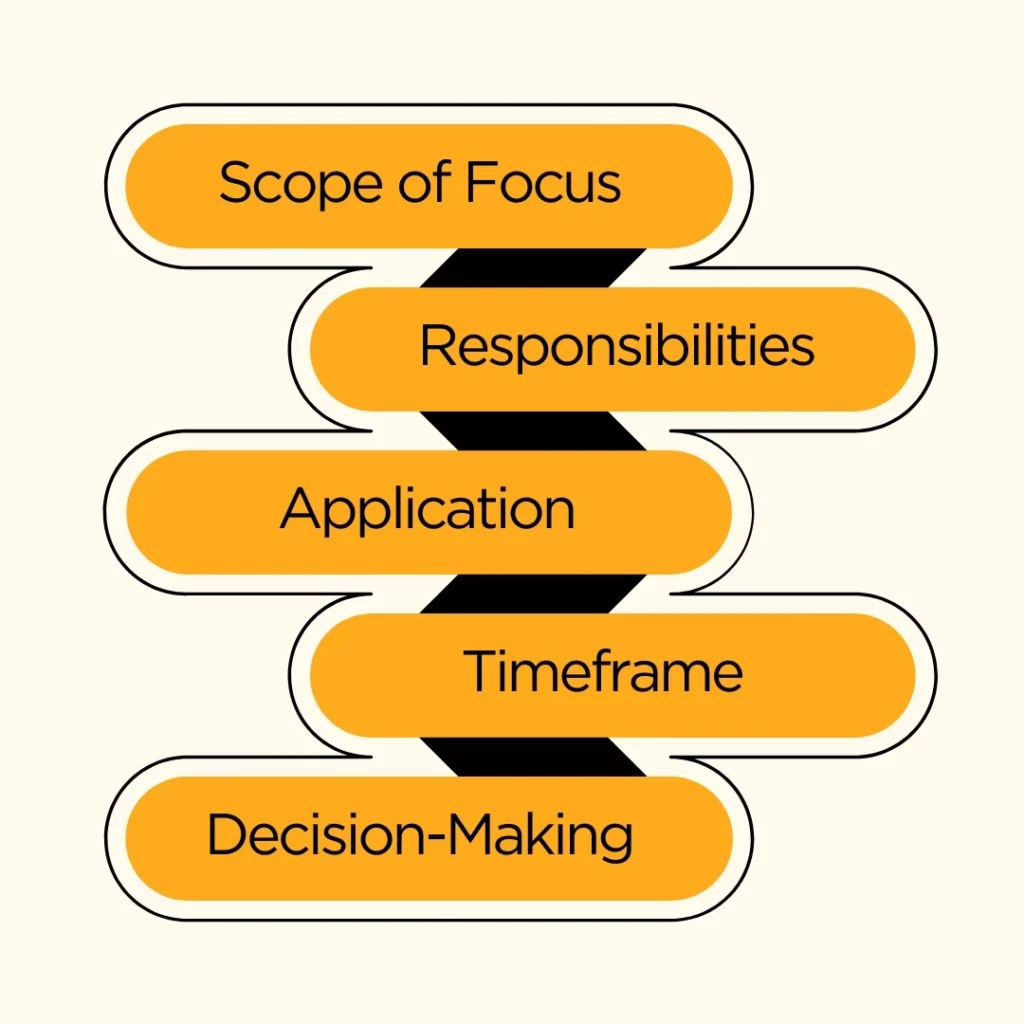
Scope of Focus
Production Management: Scope of focus is another notable difference between production management and operations management. Production management primarily focuses on the manufacturing of tangible goods.
Operations Management: Encompasses both manufacturing and service-related activities, taking a more holistic approach.
Responsibilities
Production Management: Concentrates on activities directly related to manufacturing processes, such as production planning, quality control, and capacity management.
Operations Management: Involves a wider range of responsibilities, including strategic planning, supply chain management, and coordination of various functions within an organization.
Application
Production Management: Another major difference between production management and operations management is application. Production management is mainly applied in industries where the primary output is a physical product.
Operations Management: Applicable across a diverse range of industries, including those involved in services, to ensure efficient processes and delivery.
Timeframe
Production Management: Often associated with short-term planning and execution to meet immediate production goals.
Operations Management: Involves both short-term and long-term planning, focusing on strategic decisions to improve overall organizational performance and competitiveness.
Decision-Making
Production Management: Primarily involves operational decisions related to production processes, workforce management, and resource utilization.
Operations Management: Involves strategic decisions that impact the entire organization, including product design, process optimization, supply chain management, and market positioning.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Production and Operations Management
Production management and operations management are closely linked with artificial intelligence (AI) in various ways. AI technologies can significantly enhance and optimize the efficiency, effectiveness, and decision-making processes in both production and operations. Here are some ways to justify that Artificial Intelligence plays a major role in production and operations management:
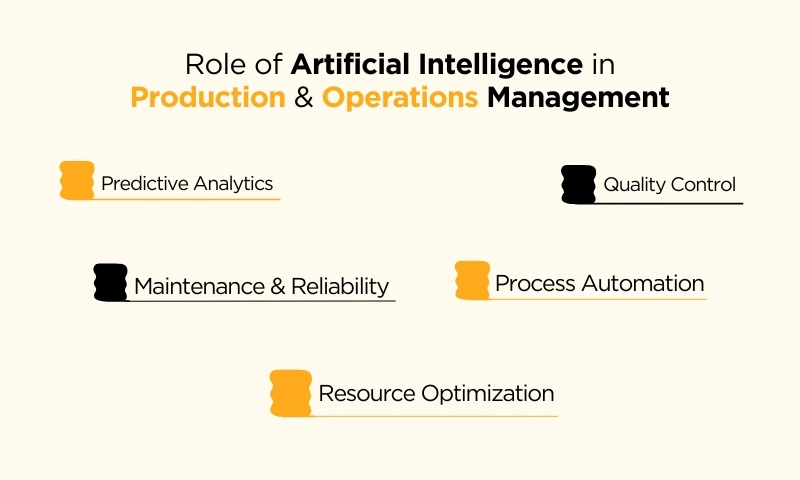
- Predictive Analytics
AI can analyze historical data and predict future trends, helping in better demand forecasting and production planning. This allows for more accurate resource allocation and inventory management.
- Quality Control
AI technologies, such as computer vision, can be employed for quality control in manufacturing processes. Automated systems can inspect products for defects more accurately and efficiently than human operators.
- Maintenance and Reliability
AI-driven predictive maintenance systems can monitor equipment performance and predict potential failures before they occur. This helps in reducing downtime and improving overall equipment reliability.
- Process Automation
AI and robotic process automation (RPA) can be used to automate routine and repetitive tasks in production and operations. This not only increases efficiency but also allows human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities.
- Resource Optimization
AI algorithms can optimize the utilization of resources such as raw materials, energy, and workforce. This leads to cost savings and increased overall efficiency in production processes.
Production Management and Operations Management: Real-time Examples
To better understand the application of production management and operations management in the real world, let’s explore some of the best real-time examples.
Toyota’s Lean Manufacturing
Toyota, renowned for its efficient production system, exemplifies the principles of Production and Operations Management through its Lean Manufacturing approach. By minimizing waste, optimizing production flow, and continuously improving processes, Toyota has been able to achieve high levels of efficiency and maintain a competitive edge in the automotive industry.
Amazon’s Fulfillment Centers
In the realm of e-commerce, Amazon’s operations management is a shining example. The company strategically locates its fulfillment centers, employs advanced automation, and utilizes data analytics to optimize the entire order fulfillment process. This allows Amazon to deliver products to customers with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
McDonald’s Supply Chain Management
McDonald’s, a global fast-food giant, showcases exemplary Production and Operations Management in its supply chain. The company maintains a finely tuned supply chain to ensure a consistent and timely flow of raw materials to its restaurants worldwide. This not only minimizes inventory costs but also guarantees that customers receive their favorite meals with consistent quality.
Tesla’s Agile Manufacturing
Tesla, a pioneer in the electric vehicle industry, employs agile manufacturing principles as part of its Production Management strategy. The company’s ability to quickly adapt to changes in market demand, implement rapid design changes, and efficiently manage its production processes has contributed to its success.
Let’s Wrap Up
In summary, while Production Management and Operations Management share commonalities in their objective of optimizing processes, they differ in their scope and focus. Production Management is specific to the manufacturing of tangible goods, while Operations Management takes a broader view, encompassing both manufacturing and service-related activities. Understanding the difference between production management and operation management is crucial for businesses to deploy the right strategies and ensure optimal efficiency in their unique operational contexts.
By recognizing the production and operations management differences, organizations can tailor their management approaches to meet the specific challenges and opportunities they face in the dynamic business landscape.



